Project Information
Buckambool Human-Induced Regeneration Project
Human Induced Regeneration
The current landholders took over Buckambool Station in 2017 with a Human-Induced Regeneration project in place. Located south of Cobar in NSW, the property is run as a successful grazing enterprise beneath the rocky ridges that dominate the area, with around 1,500 head of sheep and 200 head of cattle – depending on the season.
Before the project was established, native forest had been suppressed through a combination of factors including historic clearing, sheep and cattle grazing and a significant feral animal population. These days, clearing for pasture has stopped and the landholders have invested over $300,000 back into the property, installing new paddocks and water points that enable rotational grazing, and have made upgrades to fencing to control the feral goats that were decimating the native vegetation.
Buckambool now boasts over 9,000ha of managed open forests and woodlands of Cypress Pine and Hop Bush, with Mulga, Rosewood, Budda, Turpentine and Wilga also common. The project promotes a range of ecosystem services and biodiversity in the region.
Alongside the regenerating forest, flat cropping country now thrives, ensuring the primary grazing operation remains sustainable.
Key Benefits
UN Sustainable
Development Goals


Statistics
Methodology
Human-Induced Regeneration of a Permanent Even-Aged Native Forest – 1.1 Methodology (2013) – varied 2016
Registered ID
Date registered
June 2015
Project area
9,469 ha
Permanence
100 yrs
Location
Cobar, NSW
This project is located South West of Cobar in NSW in the Cobar Peneplain bioregion. The land consists of flat cropping country, rocky ridges and small gullies. The dominant species observed on the property from field surveys include Callitris glaucophylla, Eremophila mitchellii, Eremophila sturtii, Dodonaea viscosa and Eucalyptus populnea.
The objective of this project is to regenerate natural woodlands and shrublands. This is achieved by controlled grazing and feral animal management across the project area along with fencing upgrades. In addition to sequestering carbon, regeneration of native vegetation in the project area reverses land degradation caused by feral goats and livestock and stabilises soils reducing erosion.
The Project (EOP101263) was declared project under the ‘Human Induced Regeneration of a Permanent Even-Aged Forest 1.1’ methodology (2013 c1) (the Determination) and generates Australian Carbon Credit Units (ACCUs). This is the third version of the Human Induced Regeneration methodology.
The project has issued both Kyoto ACCUs and non-Kyoto ACCUs in accordance with the date the carbon sequestration occurred. Kyoto ACCUs are issued for all carbon sequestration which has occurred after 14 May 2013 and non-Kyoto ACCUs are issued for carbon sequestration that occurred prior to this date.
| Methodology Determination | Human-Induced Regeneration of a Permanent Even-Aged Native Forest – 1.1 Methodology Determination 2013 c1 |
| Project Declaration Date [1] | 24 June 2015 |
| Permanence Period | 100 years |
|
Baseline Period [2] (10 year period before project commencement) |
January 2000 – December 2009 |
|
Baseline management (Management during the Baseline Period) |
Suppression of development of forest cover through uncontrolled livestock grazing, uncontrolled feral animal populations. Confirmed by evidence. |
|
Modelling Commencement Date [3] (Date at which sufficient regeneration had started in the CEA) |
01 January 2010 Note: the method requires there to be some vegetation present, at the modelling commencement in order to confirm that the area has the capacity to regenerate. |
| Modelling Tool | Reforestation Modelling Tool |
| Audit | There has been 1 audit undertaken by registered Greenhouse and Energy Auditors which has confirmed the project complies with the Methodology Determination and the requirements of the CFI Act in all material respects for the periods audited. The most recent audit report was issued on the 26 May 2017. |
HIR project Carbon Estimation Areas
What are Carbon Estimation Areas?
A CEA is an area of land within a project area where the project activity or activities are being carried out to sequester carbon (for example, the cessation of mechanical or chemical clearing or management of timing and extent of grazing to enable regeneration of vegetation to forest) and for which ACCUs can be credited[4].
These are the areas where project activities occur and where carbon abatement will be modelled applying standardised estimation formulae approved by the Clean Energy Regulator. There can be one or many CEAs on a Project Area.
Each CEA must contain areas of eligible land greater than 0.2ha in size in which the project activities are implemented and which have started to become native forest through regeneration.
- Eligible Land is land that didn’t have forest cover during the baseline period (ie. the 10 years before project commencement) and which has been used or managed in a way that suppresses development of forest cover.
- A particular area of land has Forest cover if the land has an area of at least 0.2 of a hectare and has trees that are 2 metres or more in height and provide crown cover of at least 20% of the land.
Stratification of Buckambool HIR Project Area into CEAs
Stratification is the process of “demarcating the boundaries of CEAs from ineligible and non-implementation areas within a project area”[5].
There are Guidelines setting out how Project Areas are stratified into CEAs. These include rules about evidence, stratification and record keeping to support the requirements in the CFI Rule 2015 (2018 and 2019 Amendments) including key method eligibility requirements.
Stratification of the Buckambool HIR Project was carried out in accordance with the Determination and first reported to the Clean Energy Regulator for a reporting period ending 31 December 2016.[6]
A summary of the stratification of the Buckambool HIR Project is set out below:
| Project Area | 31,159 hectares |
| Number of Carbon Estimation Areas (CEA) [7] | 1 |
| Total Carbon Estimation Areas (CEA)Size | 9,402 hectares |
| Total area excluded from CEA | 21,758 hectares |
|
Excluded from CEA – Pre-existing forest cover (forest present at any time during the baseline period) |
13,301 hectares |
|
Excluded from CEA No forest potential (areas of land that do not meet the requirements of forest potential) |
207 hectares |
|
Excluded from CEA Non-project area (areas of land that are within the project area but excluded for other reason e.g. infrastructure or areas excluded for production purposes) |
8,250 hectares |
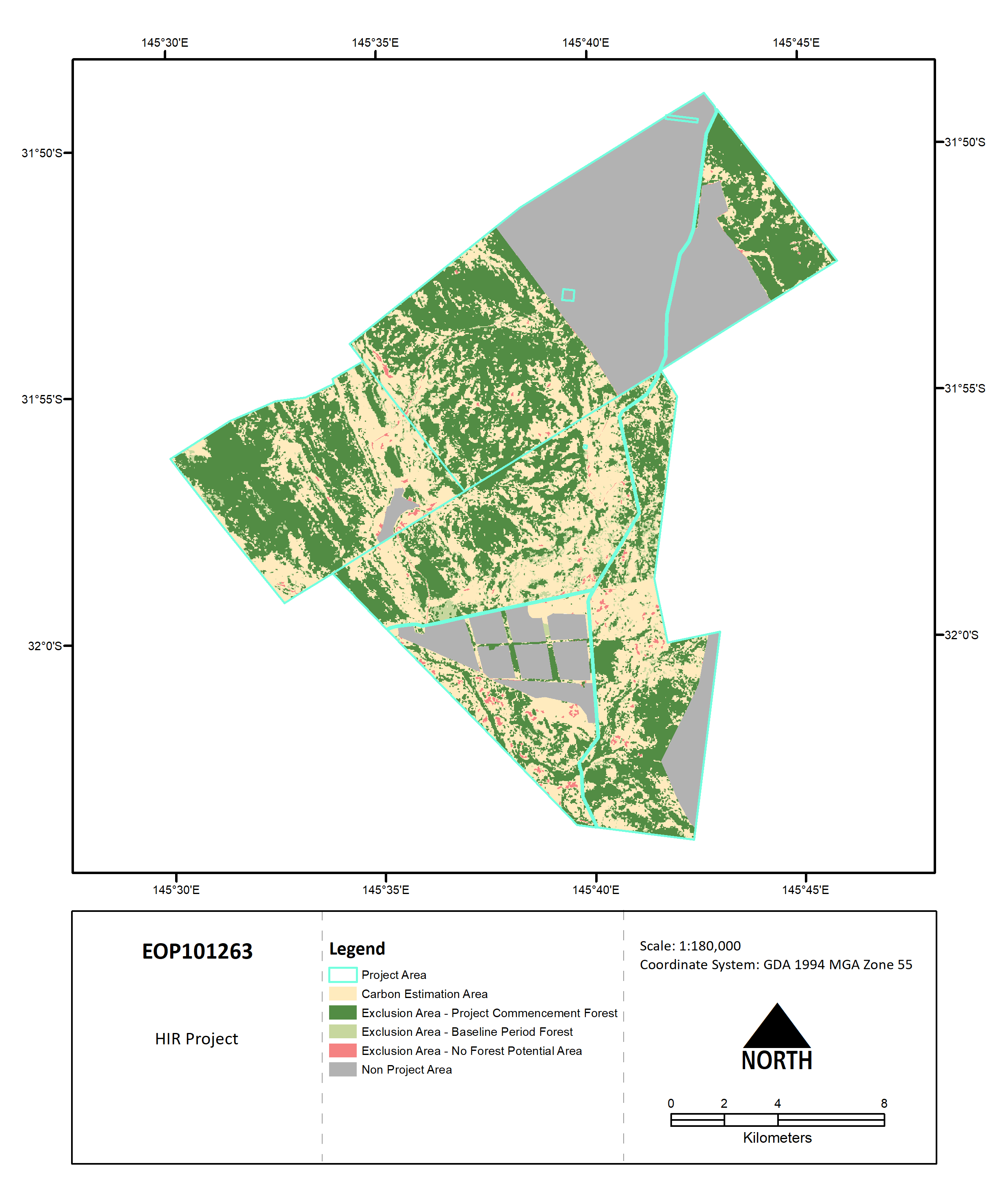
This map shows the project area boundary and the different elements of project design including the carbon estimation areas and exclusion areas. This stratification may reflect both initial stratification and subsequent revisions.
In order to inform the initial stratification of the Buckambool HIR Project in accordance with the Determination, GreenCollar carried out field surveys and data collection. This included collection of data on existing vegetation species, photos and a detailed site description.
Satellite imagery and remote sensing datasets were used to identify eligible land and exclusion areas. The extent of exclusion areas (totalling 21,758 ha), comprised of pre-existing forest cover (13,301 ha) and areas which classified as having no forest potential (207 ha). Through this process a final eligible CEA area of 9,402 ha was confirmed.
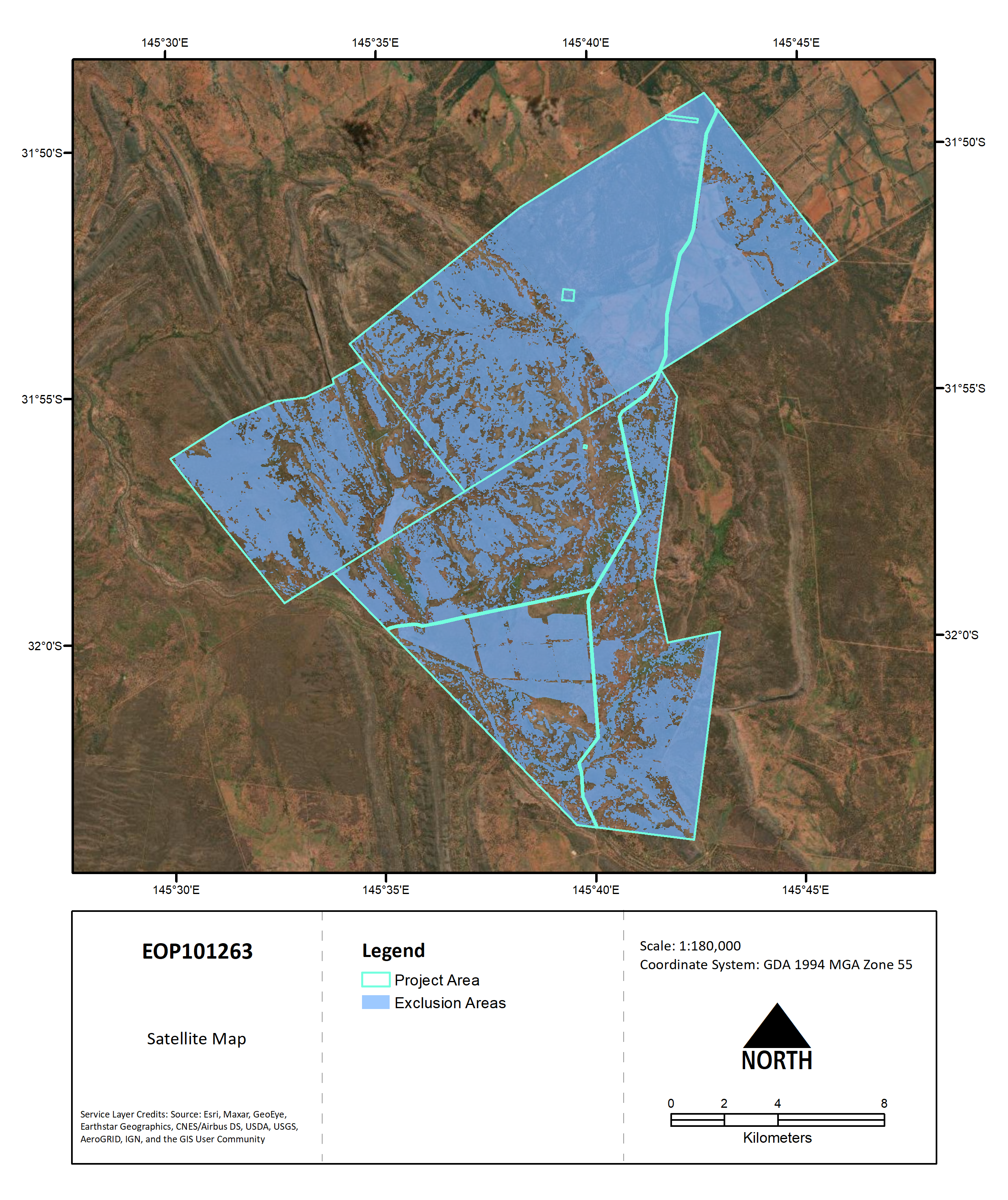
This maps shows a current satellite image of the project area. Satellite imagery and remote sensing datasets were used to identify eligible land and exclusion areas.
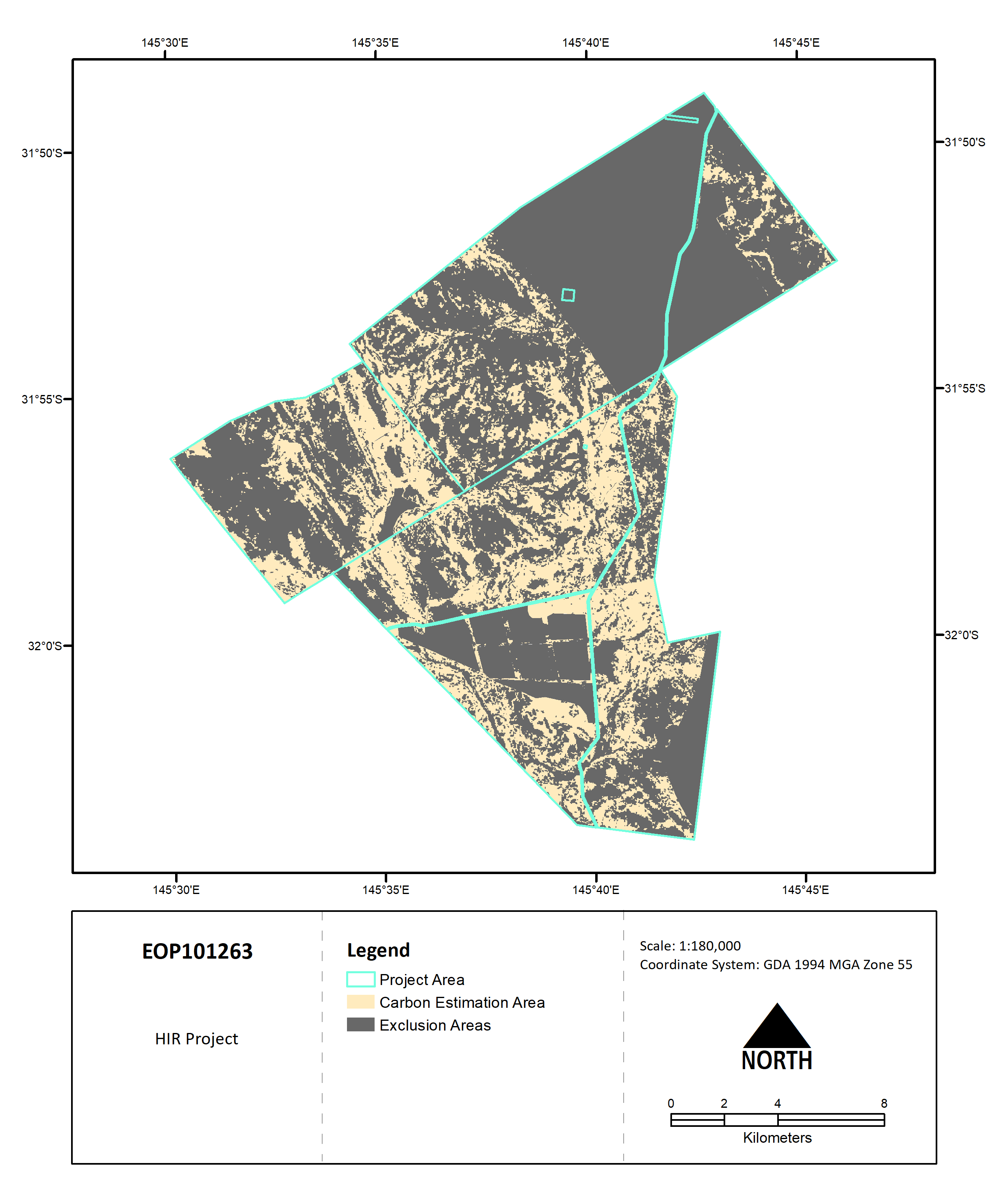
This map shows a summary of all CEA and Exclusion Areas.
Project Sequestration and Abatement
This version of the HIR Methodology required using the Reforestation Modelling Tool to determine the sequestration of carbon stocks and emissions required to calculate the net abatement amount for each reporting period. The carbon dioxide equivalent net abatement amount in relation to a reporting period for the project is taken to be the change in carbon stock for the project area less the project emissions. Any carbon stock that accumulated by the crediting start date for the project is calculated as the initial carbon stock and is removed from the calculation of abatement as the proponent is not entitled to credits for it.
See below for the average per hectare sequestration for the Buckambool HIR project.
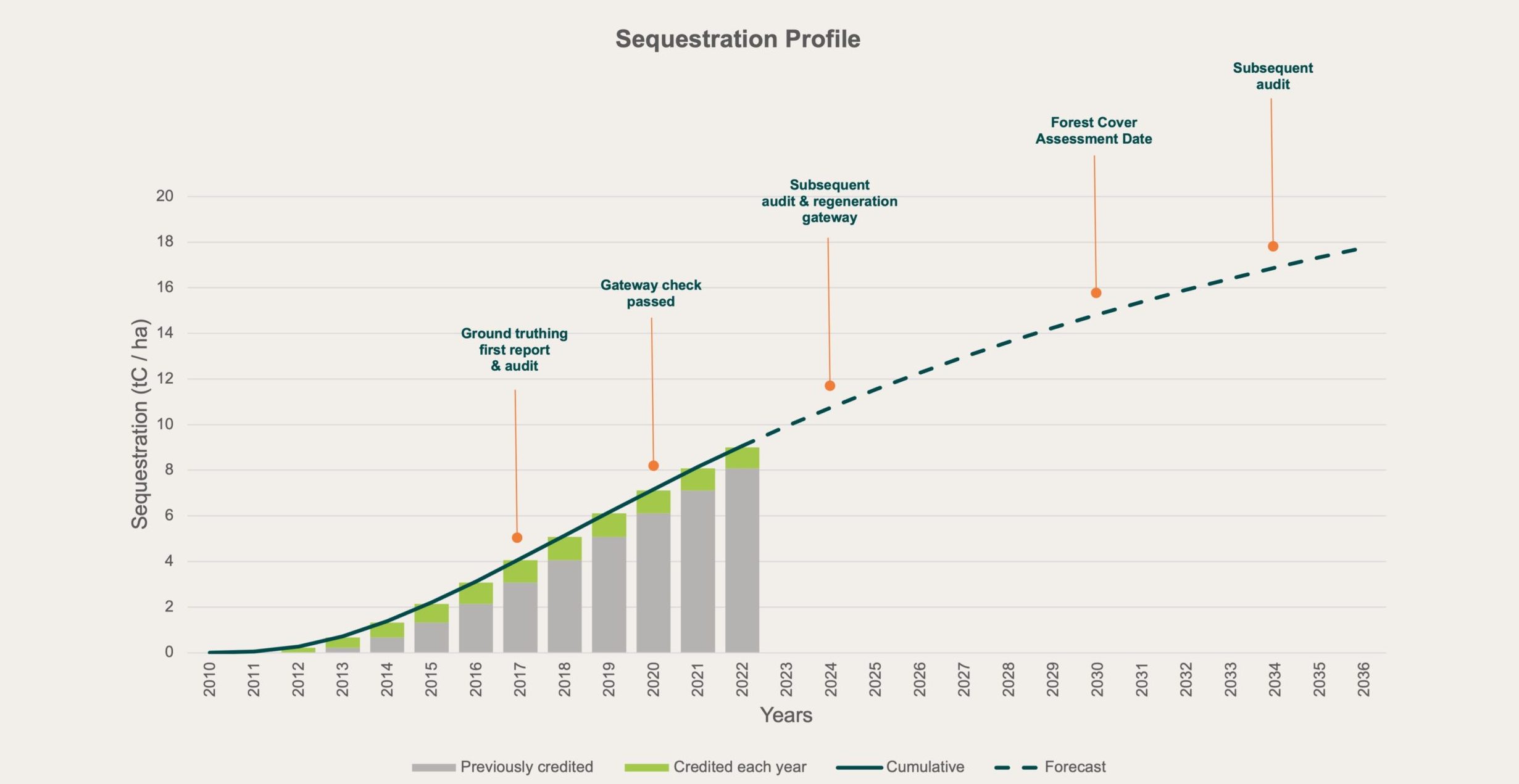
Implementation & Monitoring
The activities for the project are:
- the management of the timing & extent of grazing, and
- the management, in a humane way, of feral animals
Since project commencement these activities have been undertaken across the project area to assist the regeneration of native forest in attaining forest cover. Once the initial offsets report has been completed, GreenCollar works closely with the landholder of the project property to collect land management information every quarter. This is reviewed and reported on in each offsets report.
A summary of monitoring activities and evidence collection undertaken on this project is set out below:
- Evidence collection in relation to grazing and herd management
- Evidence collection in relation to removal and reduction of feral animals
- Evidence of fire management activities
- Evidence collection from landholder as to other land management activities as relevant
- Change detection assessments
- Repeat biomass inventory surveys to track biomass change of regenerating vegetation
- Daily fire hotspot monitoring and review of Seasonal Fire Risk
- Review of SPEI drought index
- Regeneration Gateway Checks
These surveys are currently not required under the HIR method but are implemented by GreenCollar to provide additional assurance that biophysical threats to carbon stores such as grazing, drought and fire are not negatively impacting the regeneration and to track progress of regeneration of the native forest. In addition, the data collected is utilised for broader research purposes.
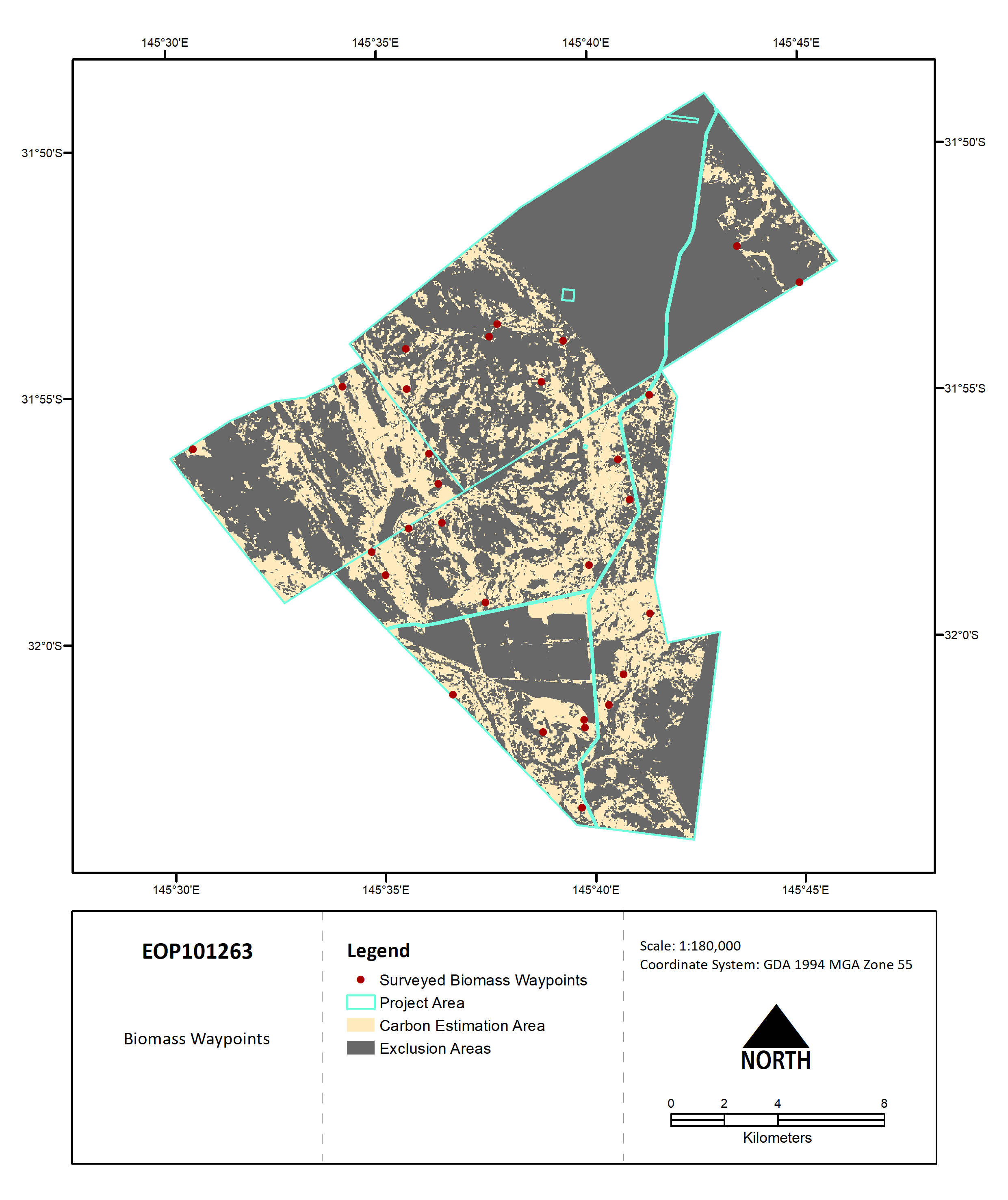
This map shows the points within the project area where vegetation biomass surveys were conducted as part of the monitoring process.
A Biomass Waypoint is a randomly allocated point within the project area where sampling data is collected.
Regeneration Checks
The Guidelines require that Proponents must provide regeneration checks at least once every five years from the start of the project’s last or only crediting period until CEAs pass their forest cover assessment date[8], and upon request by the Clean Energy Regulator.
A summary of regeneration checks required for the Buckambool HIR Project is set out below:
|
Regeneration Check: Year 6 7.5% canopy cover at 100ha scale[9] |
24 June 2020 – Completed |
|
Regeneration Check: Year 10 10% canopy cover at 10ha scale[10] |
24 June 2024 |
| Forest Cover Assessment Date [11] | 24 June 2030 |
The process and methodology includes one or more of the three evidence requirements and reporting:
- Evidence level 1: Change detection analysis, or
- Evidence level 2: Remote sensing analysis and/or
- Evidence level 3: Field data; and
- Reporting
Project Area Files
GIS shapefiles for the project can be downloaded here. These files detail the project stratification including the carbon estimation areas and exclusion areas.
[1] Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Act 2011 Section 27
[2] Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) (Human-Induced Regeneration of a Permanent Even-Aged Native Forest—1.1) Methodology Determination 2013 c1 Section 1.3
[3] Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) (Human-Induced Regeneration of a Permanent Even-Aged Native Forest—1.1) Methodology Determination 2013 c1 Section 4.5
[4] Guidelines on evidence, stratification and records 8 May 2019
[5] Guidelines on evidence, stratification and records 8 May 2019
[6] The initial stratification was reported on prior to the public release of the Guidelines on stratification, evidence and records in May 2019. These guidelines also set out administrative arrangements for projects that have previously reported, including a pragmatic approach that will be taken in situations where additional evidence is required to meet these guidelines. Additionally, the project is defined as an existing project in accordance with Section 9AA of the CFI Rule 2015.
[7] Supplementary Guidance from the Clean Energy Regulator on 19 November 2014 allows participants to choose to combine several CEAs into one CEA. For example, where small CEAs are located next to each other and share common features.
[8] Forest cover assessment date has the same meaning as that given by section 9AA(6) of the CFI Rule.
[9] Guidelines on evidence, stratification and records 8 May 2019
[10] Guidelines on evidence, stratification and records 8 May 2019
[11] Carbon Credits (Carbon Farming Initiative) Rule 2015 Section 9AA(6)








